Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound
In the realm of modern medical diagnostics, Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound (TCD) takes center stage as a noninvasive and painless ultrasound technique. It utilizes sound waves to meticulously evaluate blood flow in and around the brain, offering invaluable insights without the need for special contrast or exposure to radiation.
Physicians often recommend TCD to delve into the dynamics of blood circulation, particularly when assessing conditions such as vasospasm following a ruptured brain aneurysm, determining stroke risk in sickle cell anemia patients, investigating ischemic strokes, identifying intracranial stenosis or blockages in blood vessels, monitoring cerebral microemboli, and assessing Patent Foramen Ovale—a heart condition where a hole fails to close properly after birth.
How Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound Works
TCD operates based on the principles of ultrasound technology, a well-established and safe diagnostic method. During the procedure, a transducer is placed on the patient’s temporal bone, emitting high-frequency sound waves towards the brain. These waves penetrate the skull and interact with the moving blood cells within the cerebral vessels.
As the sound waves encounter the red blood cells, they undergo a frequency shift known as the Doppler effect. This shift is detected by the transducer, allowing the creation of real-time images and waveforms that reflect the speed and direction of blood flow. These images provide valuable information about the blood circulation within the brain, aiding in the assessment of potential abnormalities.
One noteworthy aspect of TCD is its ability to assess blood flow in different arteries, providing clinicians with a comprehensive view of cerebral circulation. This real-time monitoring capability is particularly valuable in situations requiring immediate intervention, such as during strokes or other acute neurological events.
The versatility of TCD extends beyond basic blood flow monitoring. It allows for the evaluation of specific parameters, such as pulsatility and resistance indices, contributing to a more nuanced understanding of cerebral hemodynamics. This detailed information assists healthcare professionals in diagnosing various conditions, ranging from vascular disorders to neurological diseases.
In essence, Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound functions as a non-invasive window into the intricate dynamics of cerebral blood flow, enabling precise and timely assessments crucial for effective clinical decision-making.
Advantages of Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound
A. Non-Invasiveness
Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound (TCD) stands out for its non-invasive nature, making it a patient-friendly diagnostic tool. Unlike invasive procedures that may pose risks and discomfort, TCD involves no surgical incisions or injections. The ultrasound waves are simply directed through the skin and skull, providing a safe and painless method for assessing cerebral blood flow.
B. Cost-effectiveness
In addition to its patient-friendly approach, TCD offers a cost-effective alternative in medical diagnostics. Traditional imaging methods, such as MRIs and CT scans, can be expensive and may require specialized facilities. TCD, on the other hand, is relatively more affordable, making it an accessible option for a broader demographic. This cost-effectiveness enhances its utility in various healthcare settings.
C. Versatility in Different Medical Conditions
TCD’s versatility extends beyond specific medical conditions, allowing it to play a crucial role in diverse healthcare scenarios. Whether applied in neurology, cardiology, or other medical specialties, TCD proves adaptable to different clinical settings. This broad applicability underscores its significance as a diagnostic tool with the potential to contribute to the management of a wide range of medical conditions.
Clinical Applications of TCD
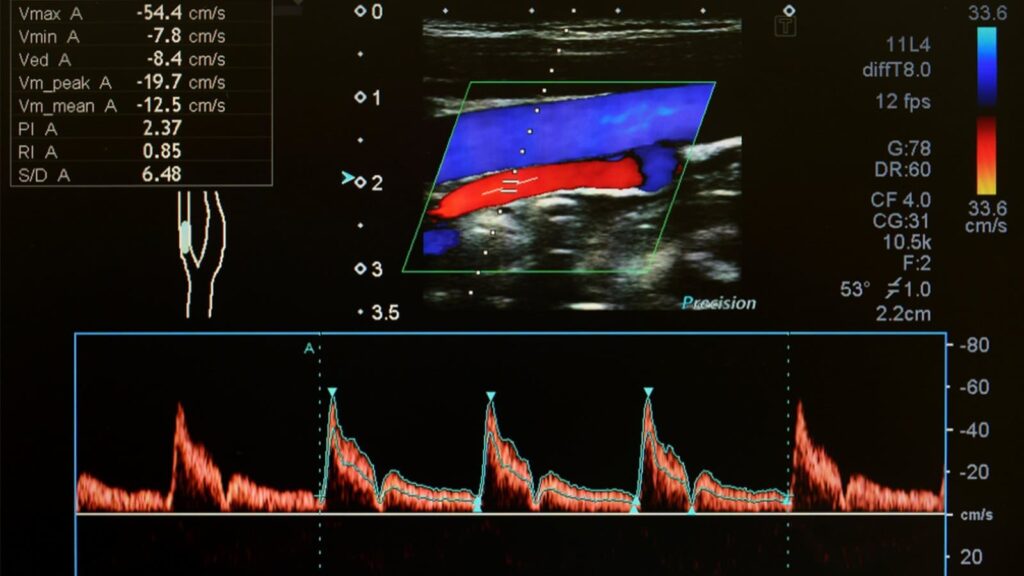
A. Detection and Monitoring of Vasospasm
B. Diagnosis of Intracranial Artery Stenosis
C. Detection of Emboli and Stroke Risk
D. Monitoring Cerebral Vascular Autoregulation
E. Detection of Right-to-Left Heart Shunt and PFO
F. Treatment Planning and Monitoring in Sickle Cell Anemia
Navigating the TCD Experience: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding and Interpreting Your TCD Results
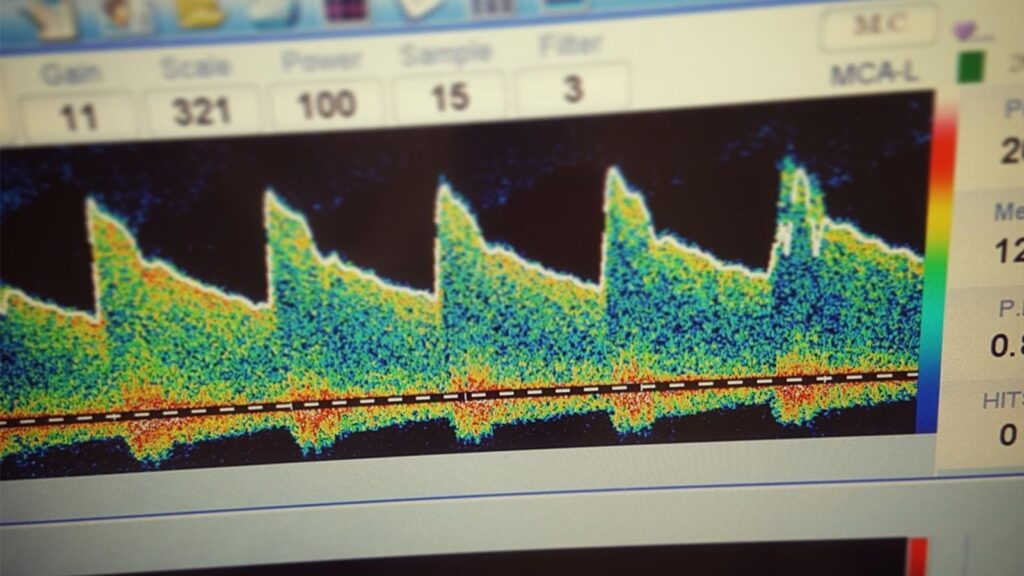
A. Receiving Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound Results
Upon completion of your transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCD), the images obtained are meticulously analyzed by a skilled radiologist or neurologist. Subsequently, a detailed report is sent to your healthcare provider who initially requested the test. This report becomes a crucial source of information for understanding the state of your cerebral health.
B. Doctor-Patient Discussion
Your healthcare provider, often your doctor or neurologist, will engage in a comprehensive discussion with you regarding the results. This dialogue aims to ensure that you are well-informed about the findings and their implications for your overall health. Any concerns or questions you may have can be addressed during this session.
C. Potential Need for Follow-Up
In some cases, a follow-up test may be recommended. This could be necessary to obtain additional views, monitor a specific medical condition for which the test was ordered, or assess the effectiveness of a prescribed treatment. The decision for a follow-up test is made with your well-being in mind, ensuring a thorough and proactive approach to your healthcare.
D. Collaborative Care Approach
The process of receiving TCD results and potential follow-up emphasizes the collaborative care approach between healthcare professionals and patients. This ensures that any necessary steps, whether they involve further testing or adjustments to your treatment plan, are taken promptly to promote optimal neurological health.
