EEG (In-Office)
In the realm of medical diagnostics, EEG (Electroencephalogram) services have emerged as a groundbreaking technology, offering in-office monitoring capabilities that provide valuable insights into brain activity.
EEG (In Office) Services involve the use of electroencephalography, a non-invasive technique that records electrical activity in the brain over time. Unlike traditional EEGs performed in hospitals, in-office services bring the convenience of monitoring brain activity in a comfortable setting.
Understanding brain function is crucial for diagnosing and managing various neurological disorders. In-office EEG services play a pivotal role in providing real-time data for accurate assessments.
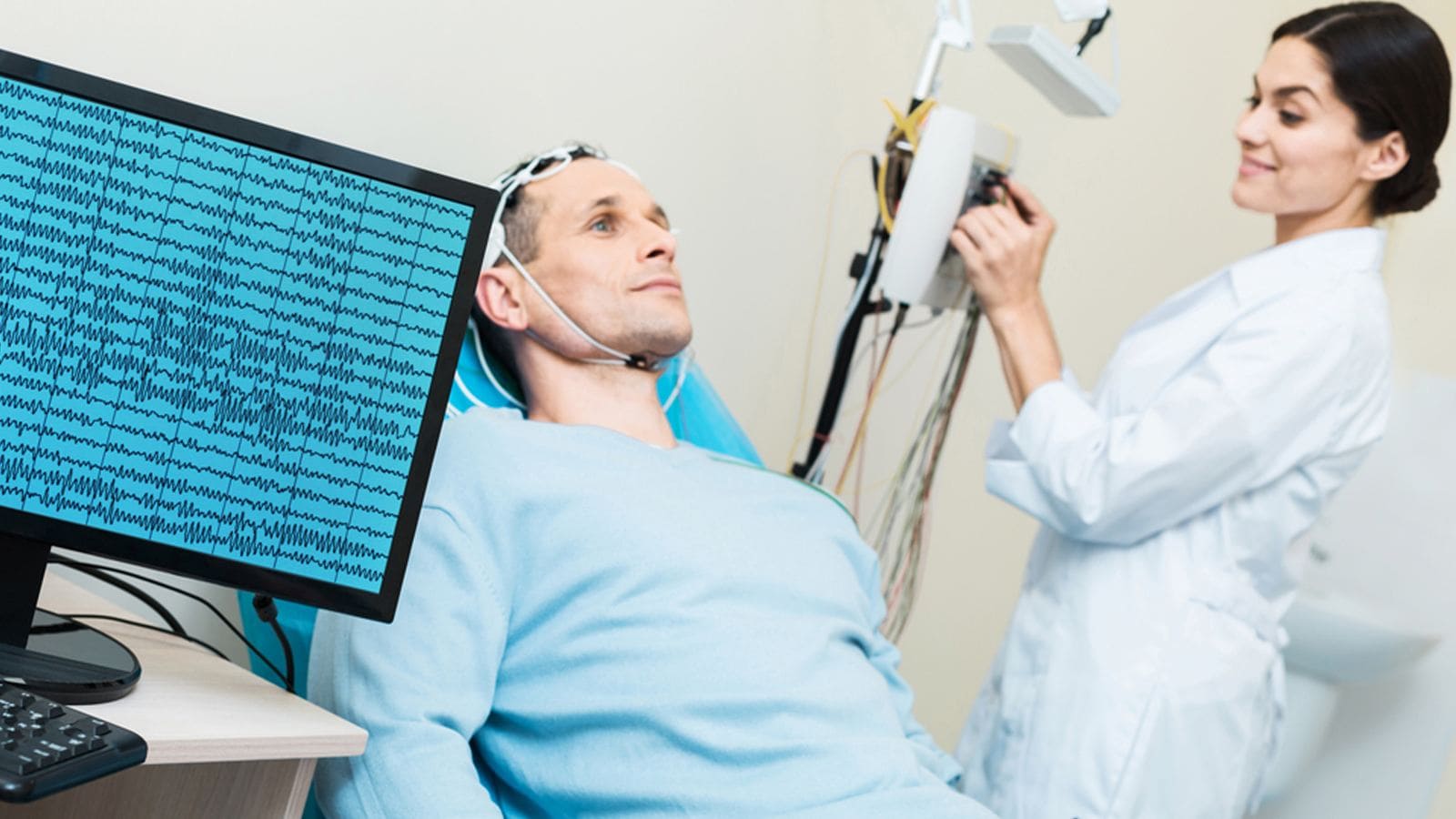
Applications of EEG in Medical Settings
Diagnosing Neurological Disorders
In-office EEGs aid in the diagnosis of conditions such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, and cognitive impairments. The real-time data allows healthcare professionals to identify abnormal brain patterns.
Monitoring Epilepsy
For patients with epilepsy, continuous monitoring through in-office EEG services helps track seizure activity, evaluate treatment effectiveness, and adjust medications accordingly.
Research and Clinical Trials
Researchers utilize EEG data to study brain function, conduct clinical trials, and develop new interventions for neurological disorders. The insights gained contribute to advancements in neuroscience.
How to Prepare for an In-Office EEG
Preparation for an in-office EEG is essential to ensure accurate and reliable results. Here are key steps to take before the test:

Proper preparation enhances the accuracy of EEG recordings and ensures a smooth testing process. For personalized guidelines, consult your healthcare provider, who will provide specific instructions tailored to your individual needs and health condition.
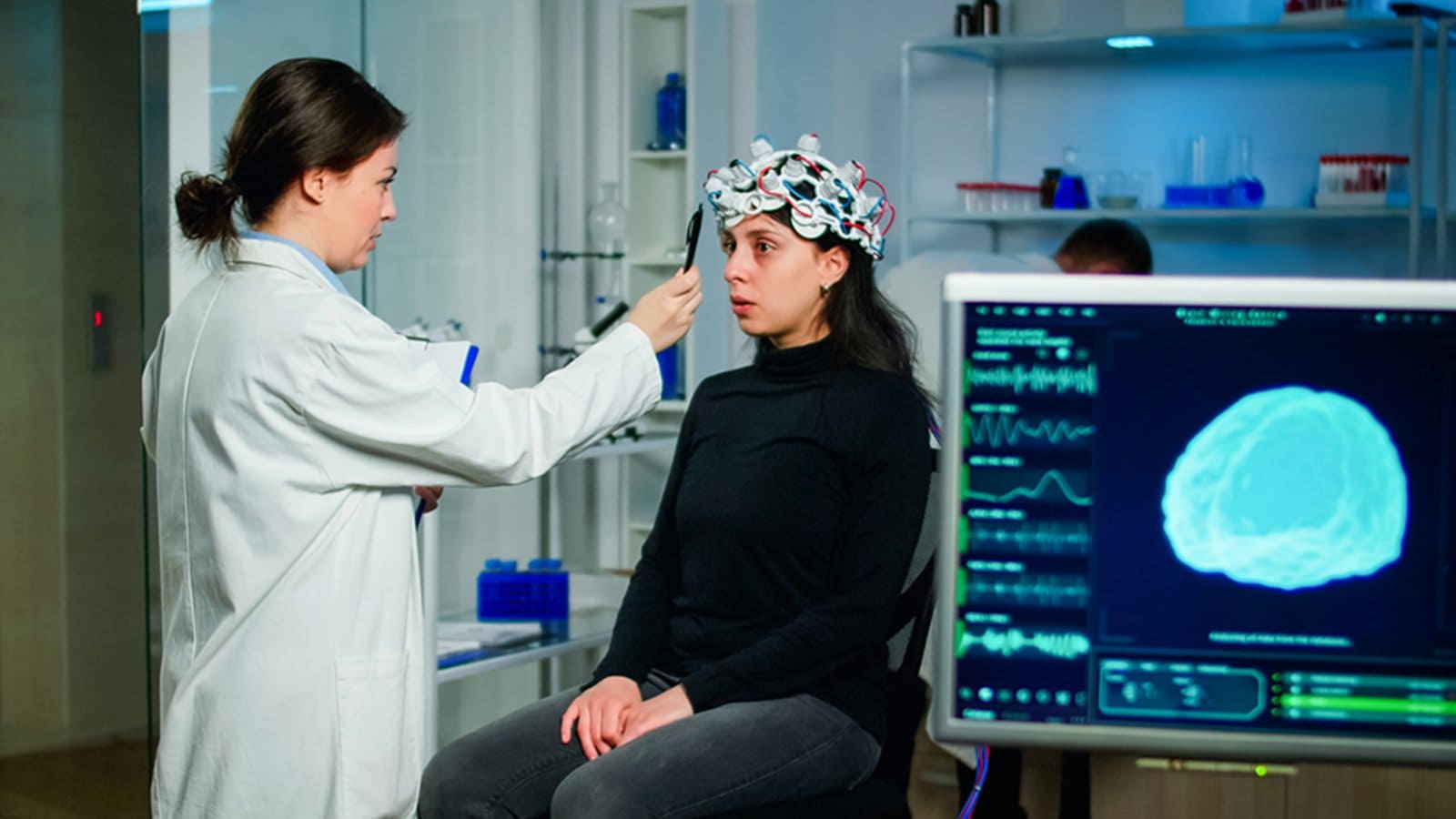
The Process of Conducting In-Office EEG
Preparation
Before an EEG session, patients are typically advised to avoid certain substances that may impact the accuracy of the readings. This includes abstaining from caffeine, as it can interfere with the brain’s electrical activity. Additionally, some medications may need to be temporarily discontinued to ensure the reliability of the EEG results.
Electrode Placement
The precise placement of electrodes on the scalp is a critical aspect of the EEG process. This step involves attaching small, flat metal discs to specific locations on the patient’s head using a conductive gel. The locations are determined based on the International 10-20 system, a standardized method for electrode placement in EEG.
Recording and Analysis
Once the electrodes are in place, the EEG machine records the electrical activity of the brain over a set period. During this recording, patients may be asked to perform specific tasks or experience controlled stimuli to provoke particular responses. This helps in capturing a diverse range of brain activities for comprehensive analysis.
Following the recording, skilled technicians and neurologists analyze the data. They examine the frequency, amplitude, and other characteristics of the recorded brainwaves. This detailed analysis aids in identifying any irregularities or abnormal patterns that may be indicative of neurological disorders.
Expanding on the recording and analysis phase, advancements in EEG technology now include features like quantitative EEG (qEEG), which provides a more detailed and quantitative assessment of brainwave patterns. This nuanced approach enhances the diagnostic accuracy of EEG, allowing for a more refined understanding of the patient’s neurological health.
Benefits of In-Office EEG Services
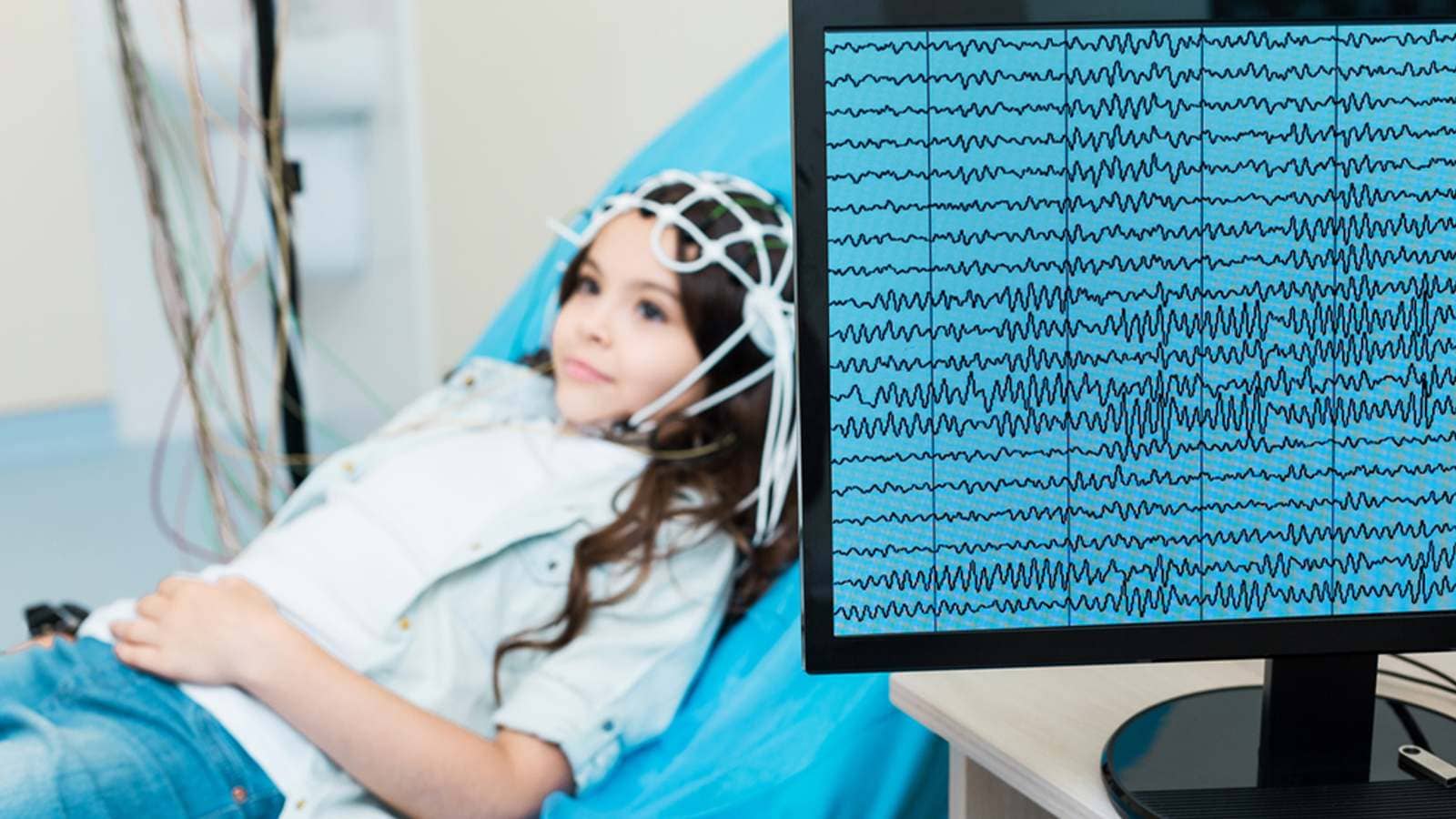

Quick and Non-Invasive
In-office EEG procedures offer the advantage of being both quick and non-invasive. Unlike other diagnostic methods, EEG does not require surgery or penetration into the body. This not only minimizes patient discomfort but also allows for repeated sessions when necessary, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s neurological status.
Real-Time Monitoring
The real-time monitoring capabilities of EEG extend beyond the diagnostic phase. Continuous monitoring proves invaluable in situations where immediate feedback is essential, such as during surgical procedures or when managing acute neurological events. This real-time insight aids healthcare professionals in making swift, informed decisions for optimal patient care.
Customized Treatment Plans
One of the significant advantages of in-office EEG lies in its ability to contribute to customized treatment plans. By capturing real-time data on brain activity, healthcare providers can tailor interventions to address specific patterns or abnormalities identified during the EEG session. This personalized approach enhances the effectiveness of treatments, potentially leading to improved patient outcomes.
Enhanced Pediatric Applications
In the realm of pediatrics, in-office EEG holds particular significance. Its non-invasive nature makes it well-suited for monitoring and diagnosing neurological conditions in children. The ability to gather accurate data without causing distress to young patients contributes to more effective management of pediatric neurological disorders.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
Compared to certain imaging techniques, in-office EEG is often a more cost-effective option. Additionally, the accessibility of EEG procedures makes them a valuable tool in a variety of healthcare settings, from small clinics to large medical centers. This accessibility ensures that a broader population can benefit from the diagnostic and monitoring capabilities offered by EEG technology.
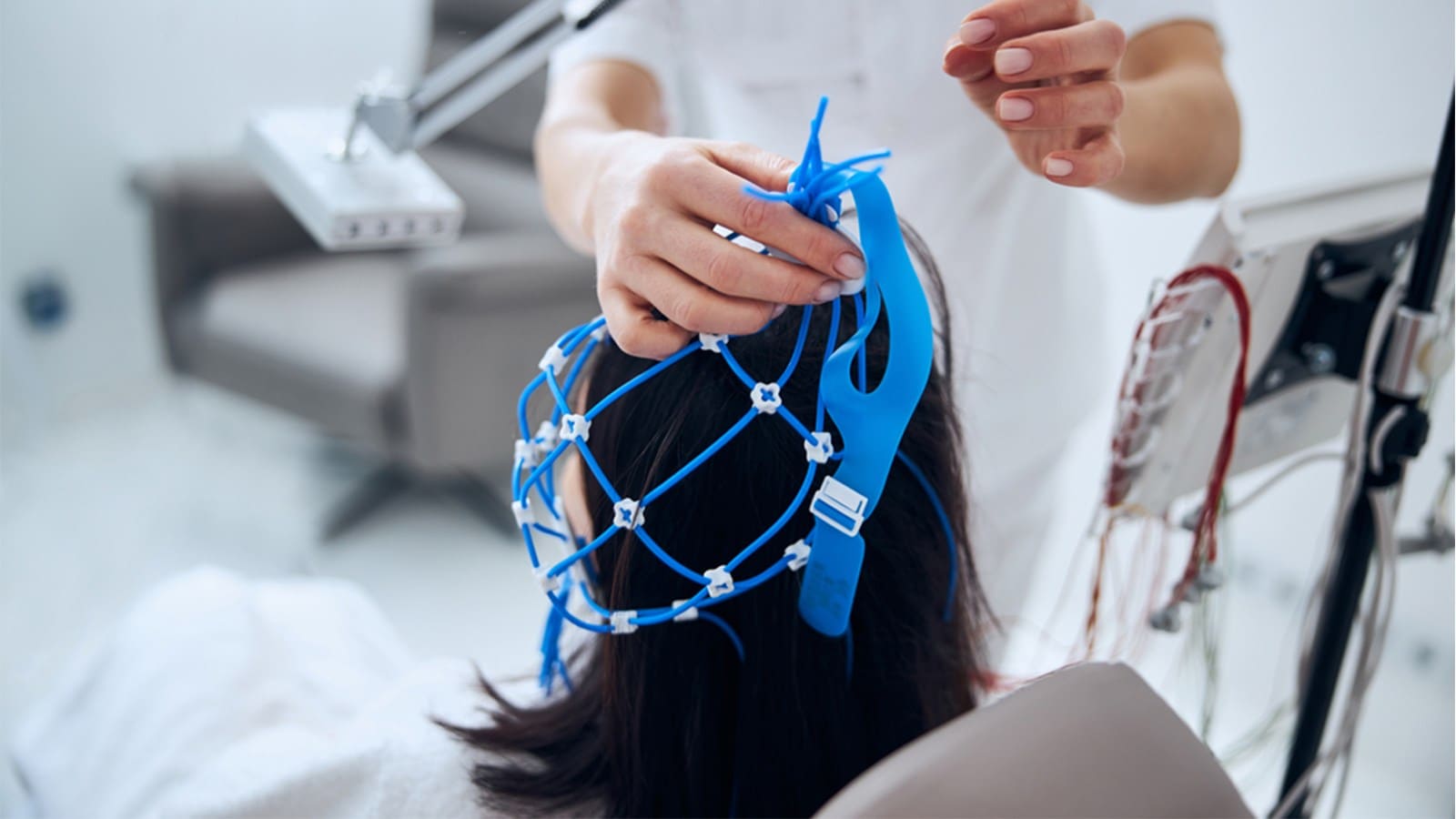

How EEG Impacts Treatment Plans
In the realm of healthcare, EEG plays a pivotal role in shaping effective treatment plans. The test has been employed since 1929, proving instrumental in detecting abnormalities in brain electrical activity associated with various disorders. The measurements obtained through EEG contribute significantly to confirming or ruling out conditions such as:
When confronted with seizure disorders, EEG aids in the confirmation of conditions like epilepsy, guiding healthcare professionals in devising targeted treatment strategies. The test’s utility extends to cases of head injury, where EEG measurements provide valuable insights into the extent of brain dysfunction. Additionally, EEG is crucial in detecting inflammation of the brain (encephalitis), tumors, and conditions causing cognitive impairments.
One of the notable applications of EEG is in monitoring brain activity during a coma, offering insights into the level of brain function. Moreover, EEG proves valuable in the context of brain surgery, where continuous monitoring helps ensure the preservation of essential brain functions.
In the evolving landscape of healthcare, EEG serves as a diagnostic tool that goes beyond confirming disorders; it actively contributes to the development of tailored treatment plans. The data obtained from EEG assessments allows healthcare professionals to customize interventions, ensuring precision in addressing the unique neurological profile of each patient.
As technology continues to advance, the integration of EEG data with artificial intelligence holds promise in enhancing the accuracy of diagnosis and treatment planning. The ability of EEG to provide real-time insights into brain activity positions it as a valuable asset in the hands of healthcare practitioners, ultimately impacting positive patient outcomes.
Comparison with At-Home EEG Services
In considering EEG services, individuals often weigh the pros and cons of in-office EEGs versus at-home EEGs.
Pros of In-Office EEG Services:
Cons of In-Office EEG Services:
Pros of At-Home EEG Services:
Cons of At-Home EEG Services:
Ultimately, the choice between in-office and at-home EEG services depends on individual preferences, medical requirements, and the specific needs of the diagnostic process. It is crucial to discuss these options with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable approach for each patient.
