Carotid Duplex Ultrasound
In the realm of cardiovascular diagnostics, a Carotid Duplex Ultrasound is a pivotal tool used to evaluate potential blockages or narrowing in the carotid arteries of the neck and their branches. This noninvasive procedure plays a crucial role in assessing the health of these arteries without the need for invasive measures, contributing significantly to early detection and preventive care.
How Does Carotid Duplex Ultrasound Work?
Carotid Duplex Ultrasound employs Doppler technology to generate a comprehensive 2-dimensional image of the carotid arteries. Utilizing a transducer emitting ultrasonic sound waves, this procedure allows for a detailed analysis of the arterial structure, identifying occlusions and determining the degree of blood flow. As the transducer is placed on specific locations and angles over the carotid arteries, ultrasonic waves penetrate the skin and tissues, echoing off blood cells. The reflected waves are then amplified, making them audible. The absence or faintness of these sounds can signify potential obstructions, providing valuable insights into blood flow dynamics and arterial health.
When is a Carotid Ultrasound Needed?
Determining the necessity of a carotid ultrasound is crucial for assessing cardiovascular health. Your healthcare provider may recommend this noninvasive procedure to investigate the presence of blood clots or plaque, including fat and cholesterol deposits, along the walls of your carotid arteries. These deposits have the potential to restrict blood flow to critical areas like the brain, face, and neck, ultimately posing a risk of stroke.
A carotid ultrasound might be necessary if:
The Doppler ultrasound aspect of the procedure allows your healthcare provider to examine:
Preparation for the Procedure
When preparing for a carotid ultrasound, there are minimal requirements for the patient. No specific preparations are necessary, eliminating the need for any dietary restrictions or lifestyle adjustments. However, it’s advisable to choose a comfortable shirt that doesn’t cover the neck and isn’t too tight. In cases where the chosen attire interferes with the examination, a hospital gown may be provided for optimal access.
It’s essential to avoid wearing necklaces or earrings that could obstruct the ultrasound procedure. These small considerations contribute to the overall efficiency and comfort of the examination. The patient’s ease during the procedure is a priority, ensuring a smooth and non-intrusive experience throughout the carotid ultrasound.

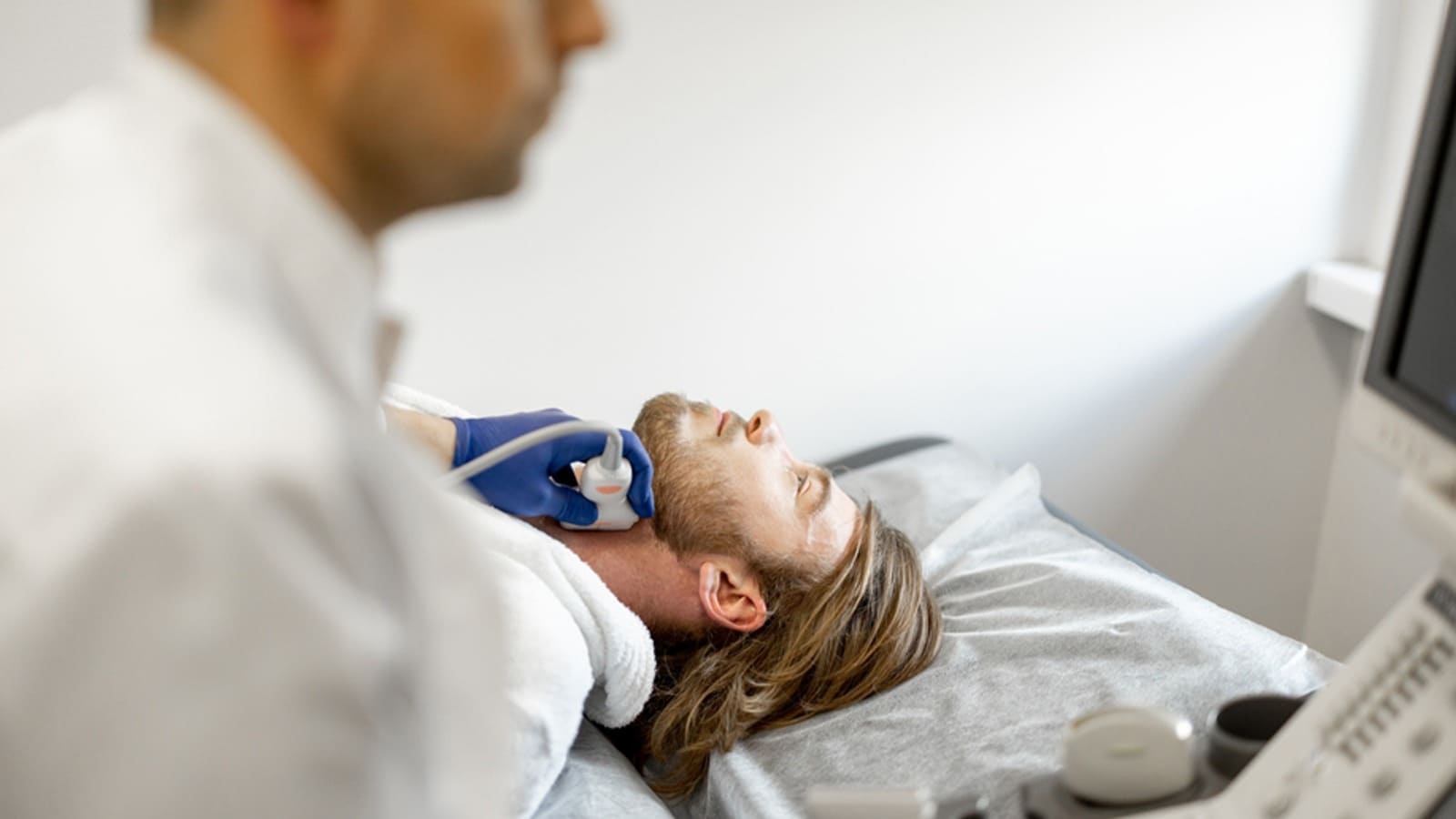
The Procedure Itself
When you undergo a Carotid Duplex Ultrasound, the vascular technologist will guide you through the process, ensuring you are comfortable and addressing any questions you may have. The procedure can be conducted with you either lying on the examination table or comfortably seated in a chair.
To facilitate the ultrasound, the technologist will apply a gentle, warm gel to the area of your neck. Following this, a transducer, a small device resembling a microphone, will be positioned over each side of your neck. While the procedure is painless, you may experience mild pressure from the transducer.
As the transducer emits ultrasonic sound waves, they penetrate your body’s organs and tissues, bouncing off the blood moving through your arteries. These sound waves create “echoes” that are then reflected back to the transducer. The electronic signals generated by the transducer convert these echoes into real-time images displayed on a television monitor. These images can be viewed immediately or captured for further analysis.
During the procedure, you might hear unusual sounds as the technologist observes and records the blood flow through your neck vessels, specifically the carotid arteries. This auditory component is a normal part of the process and contributes to the comprehensive assessment of your arterial health.
The entire Carotid Duplex Ultrasound typically lasts between 15 to 30 minutes, ensuring a swift yet thorough examination of your carotid arteries.
Interpreting Results
Once your Carotid Duplex Ultrasound is complete, the detailed study will undergo a comprehensive review by a specialized vascular surgeon. The findings will then be communicated to your physician, who will take the time to discuss and elucidate the results in the context of your overall health.
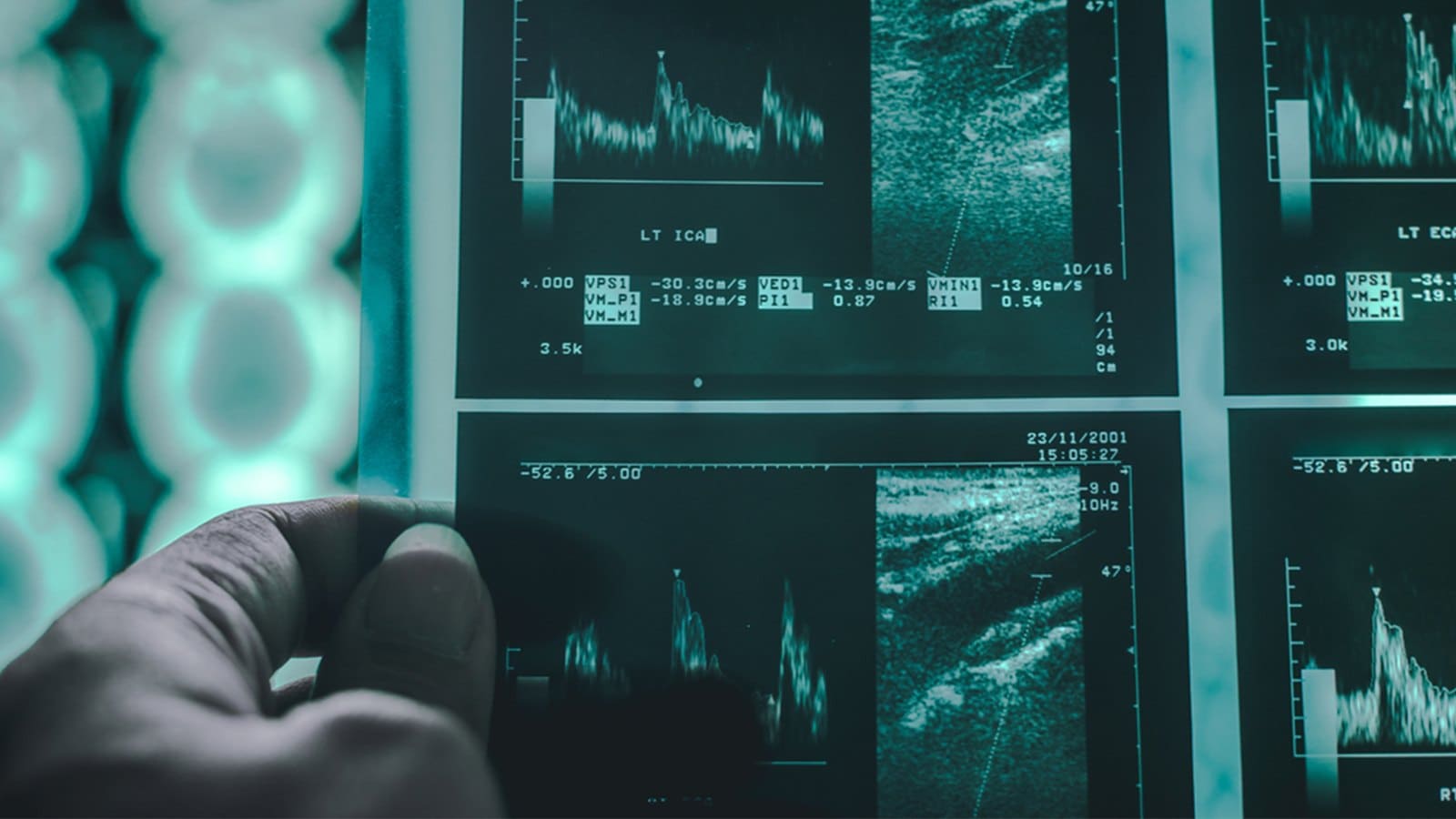
Upon receiving the results, your healthcare provider will obtain valuable insights into the condition of your carotid arteries. The evaluation typically involves assessing the presence and extent of blockages, expressed as a percentage out of 100. Let’s explore the potential scenarios:
It’s essential to note that while Carotid Duplex Ultrasound is generally accurate, there can be instances where it appears to indicate a blockage that doesn’t exist. Factors such as the experience level of sonographers and the ability of ultrasounds to detect milder problems may contribute to such occurrences. In such cases, additional imaging tests like cerebral, CT, or magnetic resonance angiography may be recommended for a more comprehensive assessment, especially when bone obstructs the ultrasound’s view of certain areas of the carotid artery.
What are the risks of a Carotid Duplex Ultrasound?
Carotid Duplex Ultrasound, being a noninvasive and safe diagnostic procedure, is generally associated with minimal risks. However, it’s essential to acknowledge potential considerations for a comprehensive understanding. Here are the key aspects to be aware of:
It’s crucial to recognize that the benefits of Carotid Duplex Ultrasound, including its role in early detection and prevention of cardiovascular risks, far outweigh these minimal considerations. The procedure remains an integral part of cardiovascular health assessment, providing valuable insights without exposing individuals to significant risks.
